
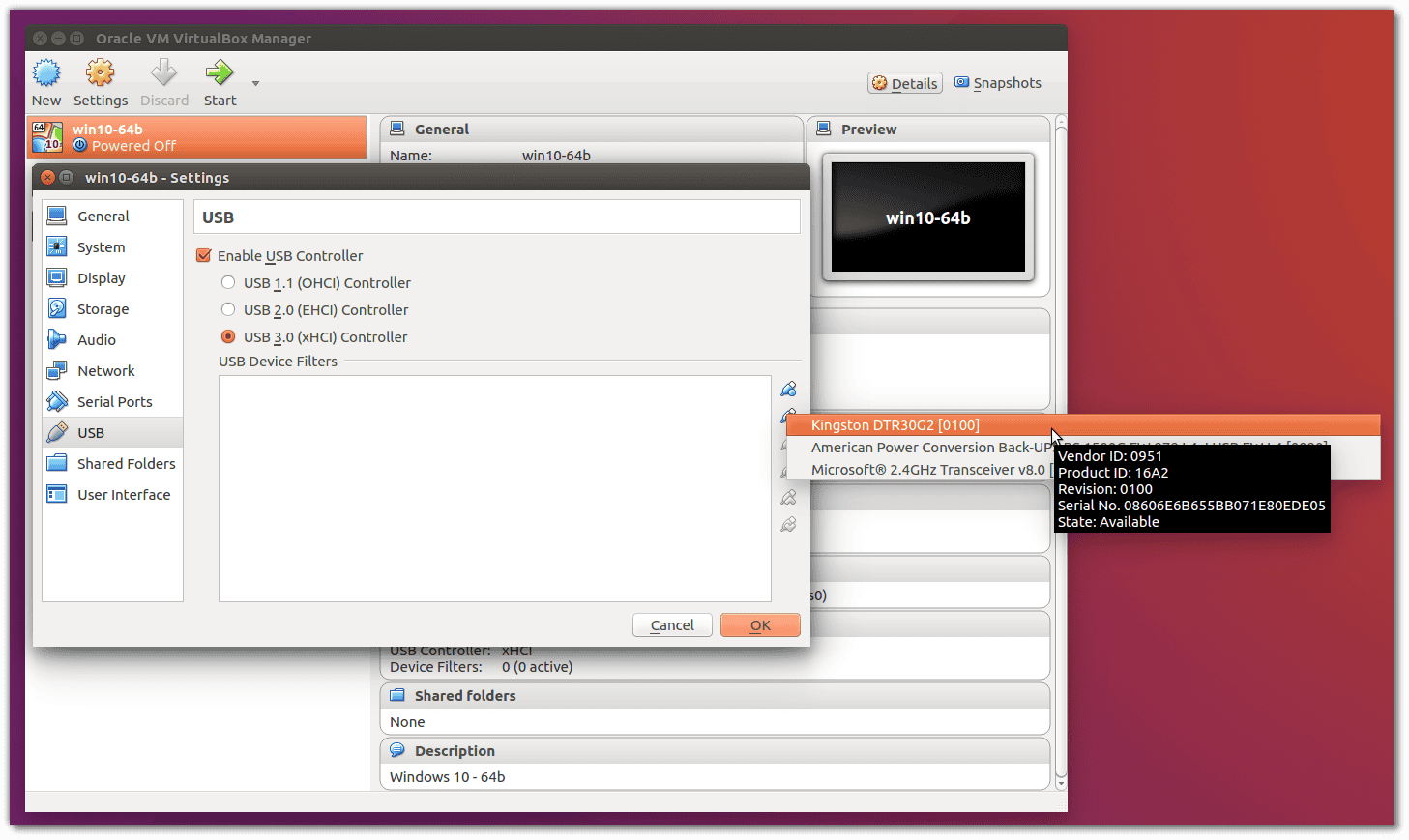
Inside you can find all the mounted folders. You can now access the shared folder, in the Guest system, to the path: Home > Devices > Computer > Media In the l ist, there should also be 999( vboxsf ). To verify if you have been added run (only for verification, not necessary): id If for example on the left of the prompt in the terminal you find written VirtualBox :~ $, it will be leo. Obviously instead of you have to insert your user in the system: This gives access privileges to the current user in the virtualbox group. To open the newly shared folder, you should give the following order command (on Ubuntu, emulated system): sudo adduser vboxsf
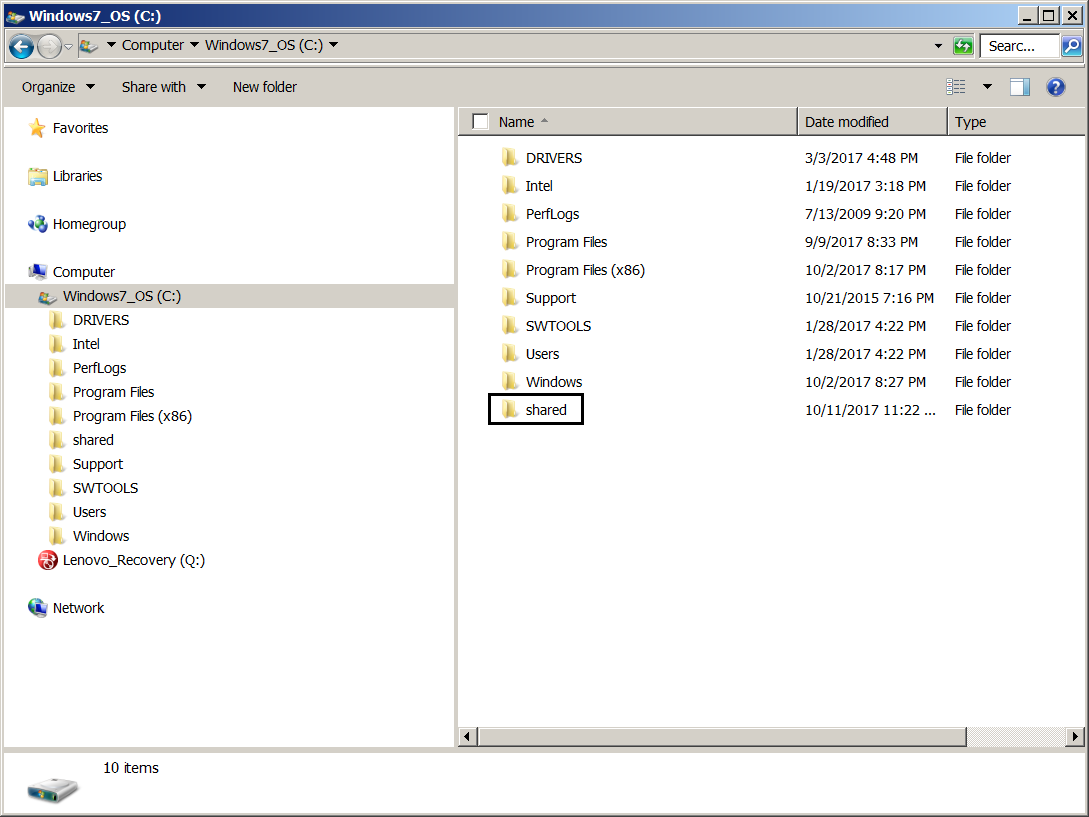
Reboot the system (the VM), and then turn it off for the next step.įrom the Host system, create the shared folder and select it from the virtual machine settings: Install the VirtualBox Guest Additions apt-get install virtualbox-guest-dkms Upload the list of packages apt-get update Open a terminal and acquire root rights with: sudo su Inside the Linux virtual machine (Ubuntu) Step 1 – Install Virtual Box Guest Additions In case you have to use Linux as Guest system, things get complicated, and you need an additional step, let’s go through it. In this way each time you start the Guest, you will find the folder mounted ‘on the network’, which refers to that of the physical system. In this case it will be enough to create a shared folder with auto- mounting, and have installed the VirtualBox Guest Additions. To do this, if you use Windows as Guest (in the VM), there are no problems. If you are using VirtualBox frequently, you will have found yourself in the situation of having to move files from the Host machine (the main system) to the Guest machine (the emulated system).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
